1. 버블정렬
가장 쉬운 정렬 알고리즘이지만 시간복잡도가 좋지 않아 실제로는 잘 사용하지 않는다. 인접한 두 데이터를 비교해서 정렬한다. 시간 복잡도 : O(n^2) 공간 복잡도 : O(n) // 하나의 배열만 사용함.
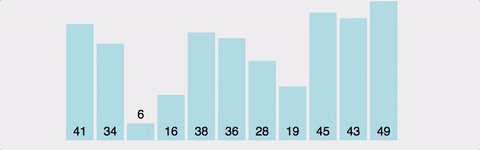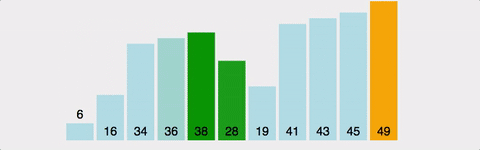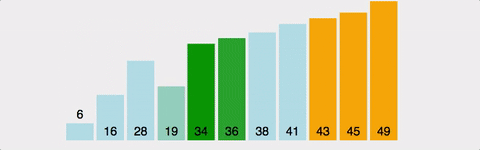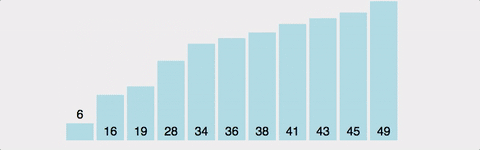
public void bubbleSort(int a[]) {
int size = a.length;
for(int i=size-1; i>0; i--) {
System.out.printf("\n버블 정렬 %d 단계 : ", size-i);
for(int j=0; j<i; j++) {
if(a[j] > a[j+1]) {
swap(a,j,j+1);
}
System.out.printf("\n\t");
for(int v : a) {
System.out.printf("%3d ", v);
}
}
}
System.out.println();
}
2. 선택정렬
전체 원소들 중 하나씩 선택하여 기준위치 이후의 원소들을 모두 비교하여 자리를 교환하는 방식 시간 복잡도 : O(n^2) 공간 복잡도 : O(n)
public void selectionSort(int a[]) {
for(int i=0; i<a.length-1; i++) {
int min = i;
for(int j=i+1; j<a.length; j++) {
if(a[j] < a[min]) { //오름차순
min = j;
}
}
swap(a, min, i);
System.out.printf("\n선택 정렬 %d 단계 : ", i+1);
for(int v : a) {
System.out.printf("%3d ", v);
}
//System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
}
System.out.println();
}
3. 삽입정렬
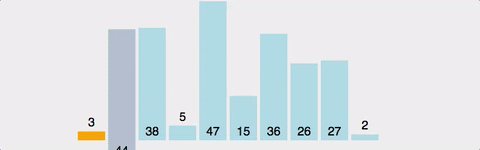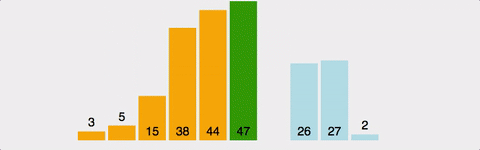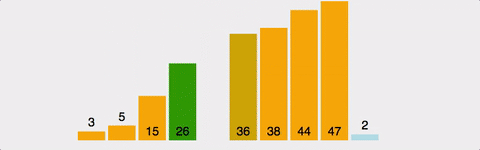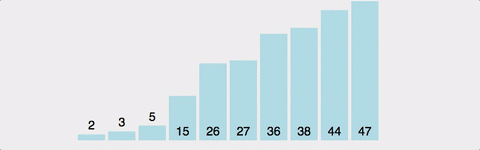
1부터 n까지 Index를 설정하여 현재위치보다 앞서 위치한 원소들을 비교하여 자신보다 작으면 그 위치에 삽입한다. 시간 복잡도 : O(n^2) 정렬이 되어 있다면 O(n) 공간 복잡도 : O(n)
public void insertionSort(int a[]) {
int size = a.length;
for(int i=1; i<size; i++) {
int temp = a[i];
int j = i;
while((j>0) && (a[j-1]>temp)) {
a[j] = a[j-1];
j--;
}
a[j] = temp;
System.out.printf("\n삽입정렬 %d 단계 : ",i);
for(int v : a) {
System.out.printf("%3d ", v);
}
}
System.out.println();
}
swap 메소드
public void swap(int a[], int idx1, int idx2) {
int temp = a[idx1];
a[idx1] = a[idx2];
a[idx2] = temp;
}