1. 합병 정렬
정렬할 리스트를 반으로 쪼개나가면서 좌측과 우측을 계속해서 분할해나가며 정렬 후 합병하는 알고리즘. 가장 많이 쓰이는 알고리즘 중 한 종류 시간 복잡도 : O(nlogn)
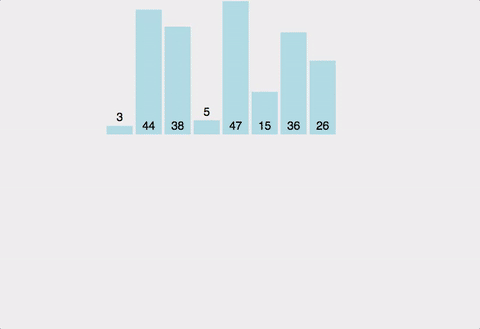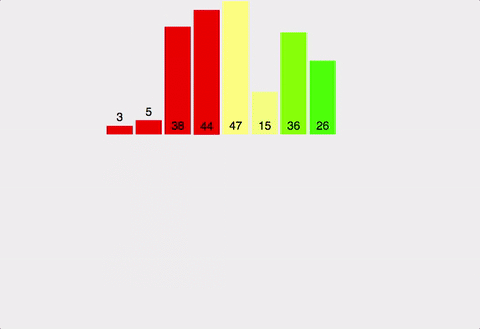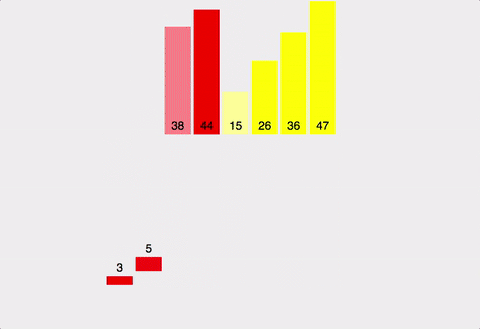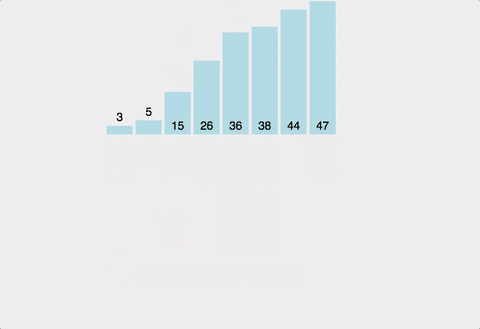
public void mergeSort(int num[], int length) {
int center = length / 2;
int leftNum[] = new int[center];
int rightNum[] = new int[length - center];
if (length == 1) return;
//왼쪽배열
for (int i = 0; i < center; i++) {
leftNum[i] = num[i];
}
//오른쪽배열
for (int i = 0; i < length - center; i++) {
rightNum[i] = num[center + i];
}
//배열체크
System.out.println("leftArray" + Arrays.toString(leftNum));
System.out.println("rightArray" + Arrays.toString(rightNum));
// 왼쪽 오른쪽 배열 나눔 재귀
mergeSort(leftNum, leftNum.length);
mergeSort(rightNum, rightNum.length);
merge(leftNum, rightNum, num);
}
private void merge(int[] leftNum, int[] rightNum, int[] num) {
int left = 0;
int right = 0;
int merge = 0;
while (leftNum.length != left && rightNum.length != right) {
if (leftNum[left] < rightNum[right]) {
num[merge] = leftNum[left];
merge++;
left++;
} else {
num[merge] = rightNum[right];
merge++;
right++;
}
}
//한쪽이 먼저 끝났을 경우
while (leftNum.length != left) {
num[merge] = leftNum[left];
merge++;
left++;
}
while (rightNum.length != right) {
num[merge] = rightNum[right];
merge++;
right++;
}
}
2. 퀵 정렬
pivot 이라는 임시원소를 하나 설정하고 pivot에 의해 작은원소 큰 원소들로 정렬된다. 재귀적 pivot은 아무것이나 잡아도 상관없지만 보통 중간 값을 선택함. 현실세계에서 데이터 정렬이 가장 빠른 형태로 가장 많이 쓰이는 알고리즘 중 하나. 시간 복잡도 : O(nlogn) 최악 시 O(n^2)
public void sort(int num[], int start, int end) {
if (start >= end) return;
int left = start;
int right = end;
int pivot = num[(left + end) / 2];
do {
while (num[left] < pivot) left++;
while (num[right] > pivot) right--;
if (left <= right) {
int temp = num[left];
num[left] = num[right];
num[right] = temp;
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(num));
left++;
right--;
}
} while (left <= right);
if (start < right) sort(num, start, right);
if (end > left) sort(num, left, end);
}